A recent report on the shipbuilding market released by market research firm Maximize Market Research indicates that driven by stricter environmental regulations and the need to replace aging vessels, the global shipbuilding market is projected to reach approximately $162.1 billion in 2024. The market is expected to grow at an average annual rate of 4.4% over the next eight years, reaching an estimated $228.8 billion by 2032.
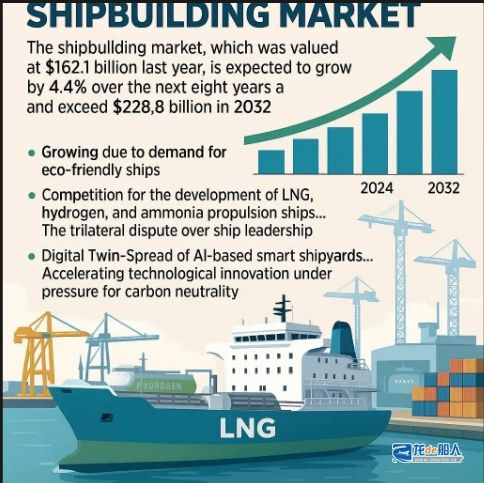
According to the report, the core driver force behind the global shipbuilding growth is the surging demand for environmentally friendly vessels. As the International Maritime Organization (IMO) strengthens emissions regulations, the shipbuilding industry is actively developing LNG-powered vessels, dual-fuel engines, hybrid systems, and next-generation fuel technologies such as hydrogen and ammonia.
The report indicates that compliance with environmental regulations is no longer optional but imperative. Ship financing, insurance, and port access permits are all tied to environmental standards, prompting shipbuilders to accelerate the adoption of drag-reduction hull designs and the implementation of eco-friendly propulsion systems such as LNG.
The industry widely recognizes that this technological transformation has transcended the mere reduction of operational emissions, becoming a core factor determining the market competitiveness of shipbuilding enterprises. Particularly with nations setting carbon neutrality targets and the pressure of carbon tax implementation, this trend is expected to accelerate.
Another driving force behind the transformation of the shipbuilding industry is the comprehensive adoption of digital technologies. The report indicates that design and simulation based on digital twin technology, automated manufacturing processes, assembly robots, and design optimization driven by artificial intelligence and machine learning are rapidly gaining traction in the shipbuilding sector.
These technological innovations significantly reduce the total lifecycle cost of vessels by shortening construction cycles, minimizing defects, and optimizing resource utilization. Vessel monitoring systems based on the Internet of Things (IoT) and data analytics are expected to become the industry standard for future maintenance and compliance inspections. As the marine energy sector expands, demand for specialized vessels such as offshore wind farm installation vessels will continue to grow.
By region, the Asia-Pacific dominates the global shipbuilding market. The report analysis indicates that China, South Korea, and Japan not only lead in mass-produced vessels such as bulk carriers, container vessels, and tankers, but also hold advantages in high-value-added vessels like LNG carriers and environmental technology innovation. Simultaneously, they demonstrate significant strengths in well-established shipbuilding facilities, skilled labor, government support, and economies of scale.
In contrast, Europe and the United States are adopting a strategy focused on the high-value-added shipbuilding market. European shipbuilders are concentrating on constructing cruise ships that meet stringent environmental standards, eco-retrofit projects, specialized vessels, and passenger vessels.
The defense sector also holds a relatively high share in Europe and North America. As countries increase investments in modernizing their naval fleets amid heightened geopolitical tensions, demand for warships equipped with advanced technologies is on the rise.


